CANNABINOIDS 101
What is our Endocannabinoid System (ECS)?
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a biological system that was first discovered in the late 1980s and early 1990s.
The ECS is largely comprised of endocannabinoids, receptors, and enzymes that are believed to help regulate a variety of functions in human including sleep, mood, memory, appetite, reproduction, and pain sensation. Scientists still have plenty of questions about the human endocannabinoid system and how it functions.
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a biological system that was first discovered in the late 1980s and early 1990s.
3 key components
The three key components of the human endocannabinoid system (ECS) are:
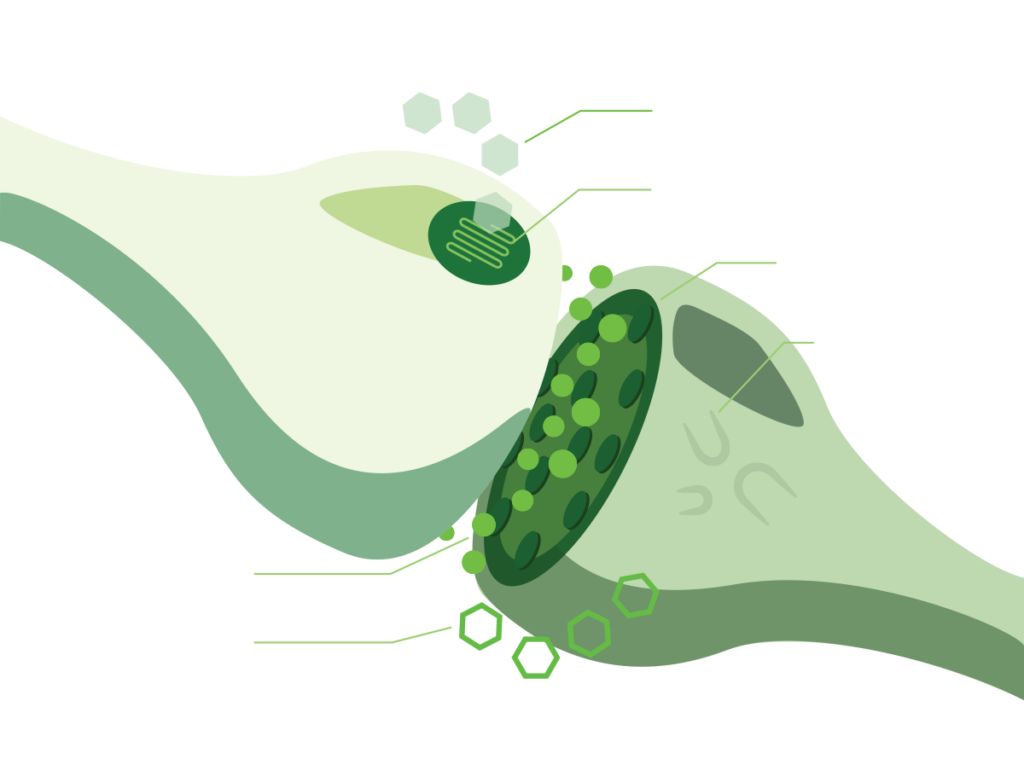
Cannabinoid receptors – located on the surface of cells
Endocannabinoids – small molecules that activate cannabinoid receptors
Metabolic enzymes – break down endocannabinoids after they are used
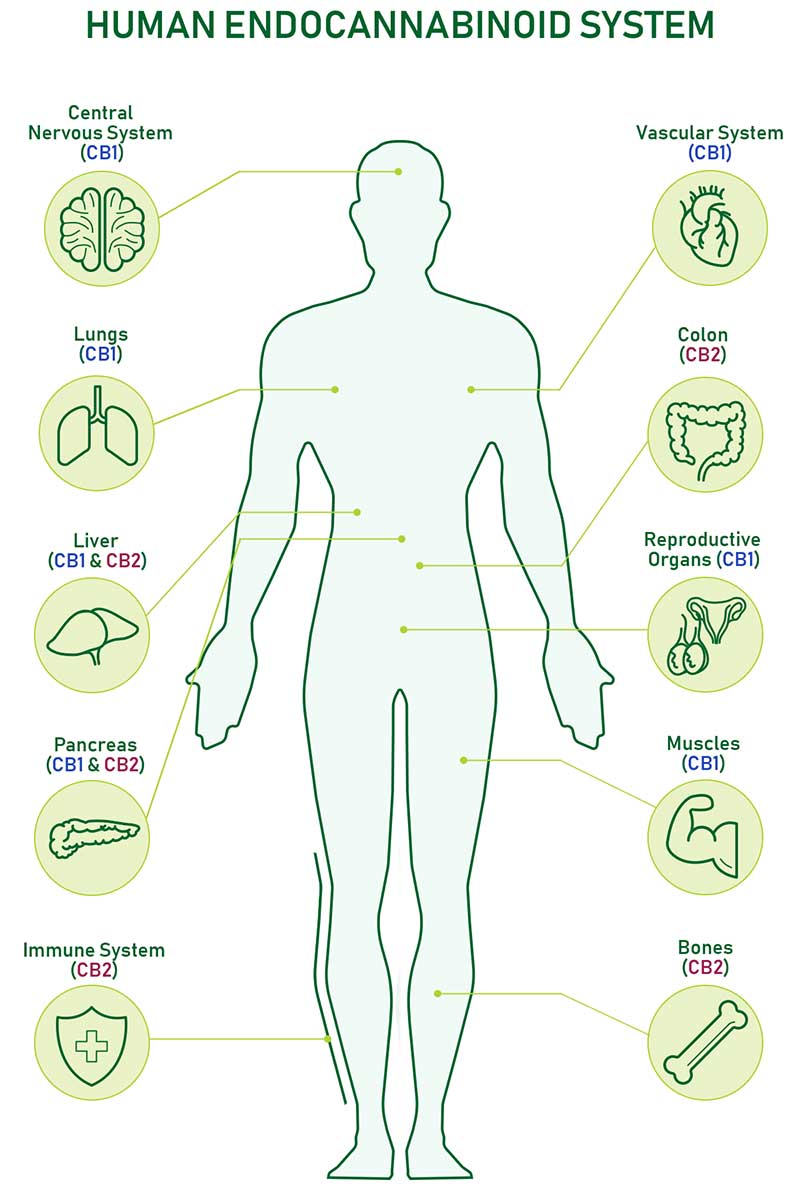
2 Major Cannabinoid Receptors
CB-1 Receptor
A receptor site located in the brain, spinal column and central nervous system that responds to cannabinoids, particularly the THC molecule, which has more of a lock-and-key type affect due to its psychoactive properties.
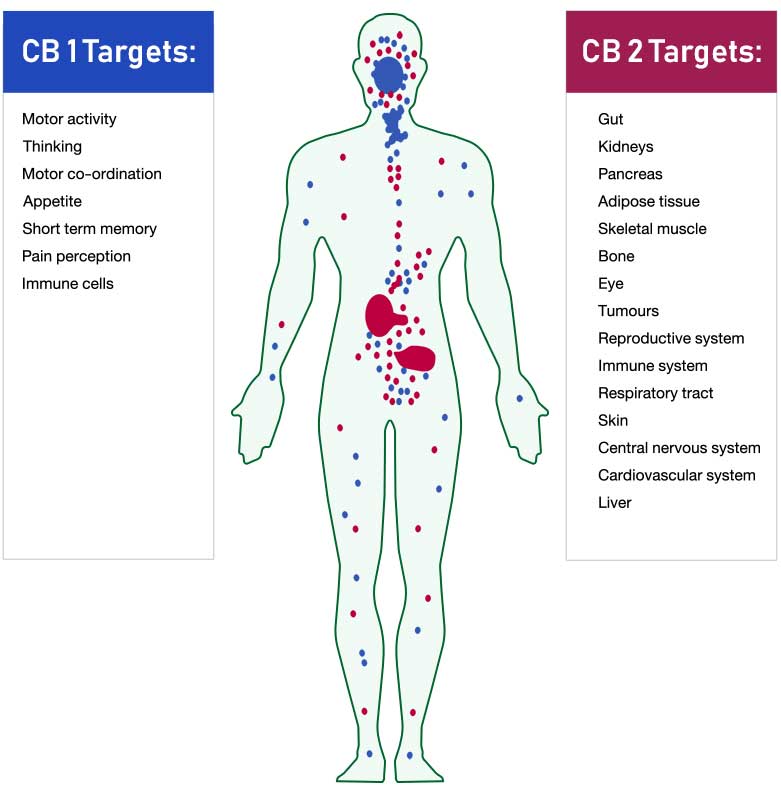
CB-2 Receptor
A receptor site located in the gut or internal organs of the body that is mainly expressed in immune tissues, which suggests the possibility that certain cannabinoids may modify the immune response or the functioning of the immune system.
What are Cannabinoids?
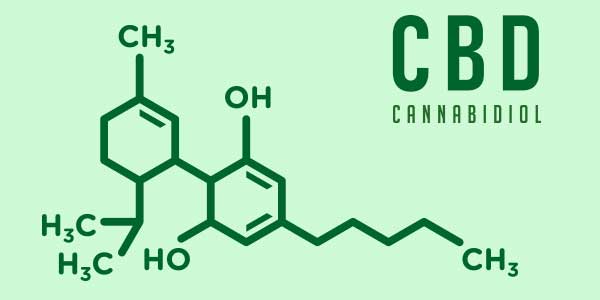
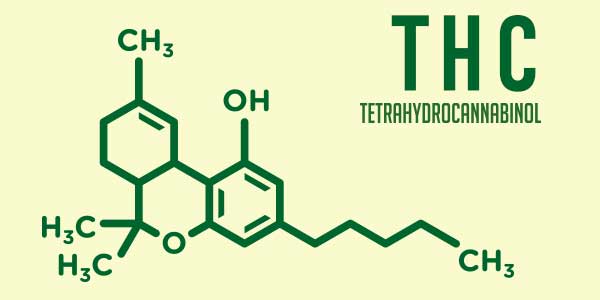
Cannabinoids (e.g., THC and CBD) are the chemical compounds discharged by cannabis flowers that provide therapeutic value to a number of ailments including pain, nausea, anxiety, and inflammation. They work by imitating compounds our bodies naturally produce, called endocannabinoids, which activate to maintain internal stability and health. In other words, cannabinoids mediate communication between cells when there is a deficiency or problem with our endocannabinoid system or if unpleasant symptoms and physical complications emerge.
Effects of Cannabinoids
When you consume cannabis, cannabinoids bind to receptor sites throughout our brain, (CB-1 Receptor) and our body (CB-2 Receptor). Different cannabinoids have different effects depending on which receptors they bind to. For example, THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol) binds to receptors in the brain whereas CBN (cannabinol) has a strong affinity for CB-2 receptors located throughout the body. Depending on a cannabis product’s cannabinoid profile, different types of relief are achievable.
The Cannabis plant contains at least 150 different cannabinoids, many of which have documented medical value. Products and strains are being developed to deliver larger doses of different cannabinoids, so it’s important to understand which types best treat your symptoms.
What are Cannabis Terpenes?
Terpenes are located in the trichome glands that produce cannabinoids such as THC and CBD, terpenes are aromatic oils that give cannabis varieties of colors as well as distinctive flavors like citrus, berry, mint, and pine. There are over 100 different types of terpenes in the cannabis plant and are believed to play an important role in varying the effects of various cannabis strains.
Some terpenes are said to promote relaxation and help with stress-relief, while others potentially promote focus and acuity. Any given terpene’s effect profile may change in the presence of other compounds, which is known as “the entourage effect.”

Most Common Types of Cannabis Terpenes
The most abundant terpene in cannabis is Myrcene. Myrcene smell often reminds of earthy, musky notes, resembling cloves. Also, it has a fruity, red grape-like aroma.
Pro Tip: For a stronger buzz from THC, eat a mango about 45 minutes before smoking. Mango contains a large amount of myrcene, so eating it prior to consuming cannabis strengthens the effects of THC and increases its absorption rate.
The second most abundant terpene in all cannabis, but not all strains necessarily contains it. Limonene gives strains a citrusy smell that much like lemons.
Regarding its therapeutic properties, limonene is known to improve one’s mood while also reducing stress. To add, research also suggests limonene has antifungal and antibacterial properties and some research has shown it to have a role in reducing tumor size.
the terpene most responsible for the recognizable skuny smell with its spicy and floral notes. Linalool is also found in lavender, mint, cinnamon and coriander. It has very strong sedative and relaxing properties.
Patients suffering from arthritis, depression, seizures, insomnia and even cancer, have all found aid in this amazing terpene.
Has a spicy and peppery note and is also found in black pepper, cinnamon, cloves, and spices such as oregano, basil and rosemary. Caryophyllene is unique in that it’s the only terpene that binds to cannabinoid receptors (specifically the CB2 receptor), which makes it an ingredient in anti-inflammatory topicals and hemp-derived creams.
In addition to its analgesic and anti-anxiety properties, some studies have cited that caryophyllene has some very promising properties when it comes to alcoholism rehabilitation.
Both of these cannabis terpenes smell like pine trees, which is where they can be found in large amounts. Other plants that are rich in pinene include orange peels, rosemary, parsley, basil, and of course, cannabis.
Pinene terpenes have an anti-inflammatory and they help improve airflow and respiratory functions, while also helping to reduce memory loss related to THC.
(AKA levomenol and bisabolol) contains a lovely floral aroma and is also found in the candeia tree and in chamomile flower.
Alpha-bisabolol is effective in treating bacterial infections and wounds and is considered a great antioxidant with anti-irritation and analgesic properties.
(AKA cineole) the primary terpene found in the eucalyptus tree. It contains recognizable minty and cool notes in its smell but most cannabis strains do not contain large amounts of it.
Regarding its medical value, eucalyptol not only offers pain relieving properties but also slows the growth of bacteria and fungus. Although it is still in the early stages in research, this terpene has shown some promising effects on Alzheimer’s as well.
a secondary terpene found mostly in flowers such as jasmine, lemongrass, and tea tree oil. Its smell is similar to a mixture of rose, citrus and apples and is described in general as having woody, citrus and floral tones.
Trans-nerolidol is best known for its antiparasitic, antioxidant, antifungal, anticancer and antimicrobial properties.
the first terpene found in hops, which explains why its aroma contains earthy, woody and spicy notes. Besides cannabis, it can be also found in clove, sage, and black pepper.
Its medical properties include anti-proliferative, meaning it prevents cancer cells from growing. It has also proved to be effective in appetite suppression, making it a potential weight loss tool. Last, similar to the other cannabis terpenes previously mentioned, it also reduces inflammation, relieves pain and fights bacterial infections.
Terpene found in a number of plants such as rosemary, basil, bell peppers, cedar and pine. Its smell is sweet and can be compared to the scent of a cypress tree.
As for its medical efficacy, it seems to be mostly beneficial in healing broken bones. Delta 3 Carene is also known to stimulate memory and helps with memory retention, which is a major point in finding a cure for Alzheimer’s disease.
smells like fir needles, musky earth and damp woodlands. Camphene is often mistaken with myrcene, which is that trademark of the typically skunky marijuana smell that most of us know.
When mixed with vitamin C, camphene becomes a powerful antioxidant, which is why it is widely used in conventional medicine as a topical for skin issues such as eczema and psoriasis. Its greatest potential lies in its ability to lower the levels of cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood, further lowering the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
contains an herbal minty scent that can be found in herbs like rosemary, mint and camphor.
This terpene serves as a great natural insect repellent by preventing diseases like the West Nile virus, being passed by ticks, fleas, mosquitoes etc. It is also widely used in Chinese traditional medicine, specifically in acupuncture.
Terpineol contains a floral-like, reminiscent of lilacs, apple blossom, and a tad citrusy. It tastes like anise and mint and is a common ingredient in perfumes, cosmetics, and flavors.
Terpineol is most known for its relaxation properties as it’s usually the one responsible for the notorious couch lock effect. Its medical benefits include antibiotic and antioxidant properties.
This terpene is named after sweet Valencia oranges, where it is found in large amounts. Its aromas and flavors are sweet citrusy and it can be used as an insect repellant, as well.
Besides cannabis, geraniol can be found in lemons and tobacco. Its smell is similar to rose grass, peaches and plums. This terpene is typically used in aromatic bath products and body lotions.
Geraniol has shown a lot of potential as a neuroprotectant and antioxidant.
